In the wealthy suburb of Highland Park, Illinois, a place where Jane Addams sometimes vacationed on the shore of Lake Michigan, a gunman with a high-powered assault rifle mowed down innocent people attending the city’s Independence Day parade. In a planned attack, from an elevated position, the gunman killed 7 people and injured 30 more. It was another preventable tragedy in a long-line of preventable tragedies in a country in which mass shootings are, outrageously, normal. The Gun Violence Archive in Washington, DC, reported on July 5, 2022, that there have been 318 mass shootings this year, ten alone on July 4 ( including the one in Highland Park). A physician, who was at the Highland Park parade and attended to the victims in the aftermath of the shootings, told a CNN reporter that the injuries he saw were “wartime injuries,” bodies “blown up by that gunfire—blown up.”
But it wasn’t a war zone. It was a parade.
Every day there is a new mass shooting (or two, or three…), and every day I am horrified, like the majority of us, who want gun legislation to stop this madness, are horrified. I can barely read the news anymore for the horrendous stories of senseless gun violence, story after story of people murdered by men with military-grade weapons designed for the battlefields of war.
 Someone asked me what Jane Addams would think about this constant violence, about people gunned down in churches, grocery stores, public spaces, and schools. Jane Addams, a pacifist, would be heartsick. She would be in disbelief that she had worked so hard to get small children out of the factories and into classrooms, only to see that 100 years later children are not safe in their schools. She would be disgusted, like she was disgusted by the lynching of Black Americans in her era. She would be shocked, like she was shocked over the unthinkable deaths of more than 600 people, many of them children, burned alive in 1903 in the Iroquois Theatre Fire in Chicago because fire safety laws went unenforced. Most importantly, she would be furious with the inaction of our leaders and would turn that fury into action. If she were alive today, she would be lobbying in Springfield and in Washington, demanding change.
Someone asked me what Jane Addams would think about this constant violence, about people gunned down in churches, grocery stores, public spaces, and schools. Jane Addams, a pacifist, would be heartsick. She would be in disbelief that she had worked so hard to get small children out of the factories and into classrooms, only to see that 100 years later children are not safe in their schools. She would be disgusted, like she was disgusted by the lynching of Black Americans in her era. She would be shocked, like she was shocked over the unthinkable deaths of more than 600 people, many of them children, burned alive in 1903 in the Iroquois Theatre Fire in Chicago because fire safety laws went unenforced. Most importantly, she would be furious with the inaction of our leaders and would turn that fury into action. If she were alive today, she would be lobbying in Springfield and in Washington, demanding change.
So, of course, I wondered if Jane Addams had any wisdom to impart on the subject of firearms and gun control. And as is always the case when I search the Jane Addams Digital Edition for answers to our modern problems or consolations for our current sorrows, I find in the words she left us nuggets of wisdom, truth, prescient observation, astute analysis, and sane advice. What I was not ready for this time, however, was the setting—Highland Park, Illinois—of the first nugget I found when I starting searching for “guns” and “gun control” and “firearms” in Jane Addams’s papers, dated from 1901-1931.
Below is a sampling of what I found. Some of it is eerie in its relevance:
On Dec. 21, 1903, two armed cavalry soldiers, who had deserted their post at Fort Sheridan, held up a hotel clerk and guests in Highland Park, Illinois, at gun point and robbed them of cash and personal possessions. Upon hearing the news, Howard H. Gross, a Chicago attorney, advocated repeal of the Chicago ordinance, passed in 1881, which made it unlawful “for any person within the limits of the city to carry or wear under his clothes, or concealed about his person, any pistol, colt or slung shot, cross knuckles, or knuckles of lead, brass or other metal, or bowie knife, dirk knife or dirk, razor or dagger, or any other dangerous or deadly weapon.” Jane Addams weighed in on the suggestion the following day, declaring it “a most pernicious idea.”

Lawlessness would only be encouraged by such a measure. Enforcement of the existing laws is the proper remedy for crime.
In 1907, the Peace Association of Friends published a pamphlet that asked the question: “Do We Want Rifle Practice in Public Schools?” The effort was a response to a growing military preparedness movement in the United States in which advocates argued that children should conduct military drills in school. Jane Addams, who had served three years on the Chicago Board of Education, was not having it and offered this statement for publication:
I am of course shocked at any proposition to introduce rifle practice into the public schools. The increasing number of accidents and murders due to the totally unnecessary and illegal “carrying of concealed weapons,” makes it difficult to understand why familiarity with fire arms should be encouraged. If war is to continue, at least let us insist that the use of fire arms shall be confined to the soldier, as strictly as the surgeon’s knife is limited to the man professionally prepared to use it.
In an article about juvenile delinquency published in the Ladies’ Home Journal in 1909, Addams wrote:
There is an entire series of difficulties directly traceable to foolish and adventurous persistence in carrying loaded firearms. The morning paper of the day on which I am writing records the following:
A party of boys, led by Daniel O’Brien, thirteen years old, had gathered in front of the house, and O’Brien was throwing stones at [Niezgodzki] in revenge for a whipping that he had received at his hands about a month ago. The Polish boy ordered them away and threatened to go into the house and get a revolver if they did not stop.
Pfister, one of the boys in O’Brien’s party, called him a coward, and, when he pulled a revolver from his pocket, dared him to put it away and meet him in a fist fight in the street.
Instead of accepting the challenge [Niezgodzki] aimed his revolver at Pfister and fired. The bullet crashed through the top of his head and entered the brain. He was rushed to the Alexian Brother’s Hospital, but died a short time after being received there. [Niezgodzki] was arrested and held without bail.
This tale could be duplicated almost every morning; what might be merely a boyish scrap is turned into a tragedy because some boy has a revolver.
In 1927, during Prohibition and much gang violence in Chicago, Addams published an essay that appeared in The Prevention and Cure of Crime, Discussed by the American Crime Study Commission. In that essay, she argued:
The sale of arms should be prohibited, for if a criminal has a gun he will shoot, and that he will try to shoot first, when in danger of arrest is perfectly obvious. We have had a great deal of shooting in our neighborhood in Chicago in connection with bootlegging. Illicit liquor is stored in empty warehouses, in stores and in the basements of disused houses. Bootleggers are much afraid of being detected not only by Federal officers and the police, but by the hijacker—the man who steals goods which are already illicit, so it is almost impossible to arrest him as a thief.
For all of these reasons the bootleggers employ lookouts to protect their goods, sometimes blocks away, and many of them are boys and very young men. Of course, many of these boys are armed. In fact, they do not like the job unless they are armed. They know that not only the hijackers, but the Federal officers and the police are armed, and in the spirit of sheer excitement they also wish to be armed “to the teeth.” Of course, the whole situation becomes dangerous to the community, perhaps most of all to the innocent passer-by.
In a statement supporting the presidential candidacy of Herbert Hoover in 1928, Addams argued:
What the prohibition situation needs first of all is “disarmament,” if this necessitates federal control of the sale of firearms so much the better, but whatever is necessary for the final result, the government agents should promptly be taught some other method than those of gunmen. That the police of the Irish Free State established immediately after the evacuation of the English Black and Tans and after Ireland’s civil war, could go unarmed in the midst of a population still carrying “concealed weapons,” encourages me to believe that brave and conscientious men may be found in America who realize that it is their business to bring the culprit to court.
In a speech at the Conference on the Cause and Cure of War in Washington, D.C., in January 1931, Jane Addams, clear and loud as a clanging bell, said:
About two years ago, a bill was introduced into the legislature of Massachusetts, in an attempt to control banditry, which has developed so rapidly into our American cities, by curtailing the manufacture as well as the purchase of firearms. While this bill was being discussed, it is said that a telegram came from Washington, stating that such legislation was contrary to the National defense policy, that wished the manufacturing of firearms to go on at a good pace, so that in time of war, arms might be easily available.
We have not gotten to the point of discussing this in Chicago, or reducing it to law, but you all know very well that our situation would be enormously improved in every great city, if some such law were passed.
Our thugs are armed and our policemen are armed, so it is largely a question of who shall shoot first; one sometimes longs for the English police who carry no arms…
Dear Jane Addams, please come back to help us. Please. We need you.
By Stacy Lynn, Associate Editor
Sources: www.gunviolencearchive.org; John W. Leonard, ed., The Book of Chicagoans: A Biographical Dictionary of Leading Living Men of the City of Chicago (Chicago: A. N. Marquis & Co, 1905), 247; “Soldiers Hold up Clerk in Hotel,” The Inter Ocean (Chicago), Dec. 22, 1903, p. 2; and Respect for Law, January 3, 1901; Statement on Carrying Concealed Weapons, December 21, 1903; Address at Memorial for Teachers Who Perished in the Iroquois Theatre Fire, January 16, 1904 (excerpt); Statement on Rifle Practice in Public Schools, 1907-1908; The Bad Boy of the Street, October 1909; Problem of Crime Unsolved, Let Us Start at It Anew, May 13, 1927; Draft of Statement Endorsing Herbert Hoover, October 23, 1928; What is Security? Conference on the Cause and Cure of War, 1931; all in Jane Addams Digital Edition.





















 Thanks to
Thanks to 
 The onset of a brutal global war in the summer of 1914 shocked Jane Addams and other American pacifists who were certain their cause was gaining widespread acceptance. “Nobody who was not a mature person…can realize now how remote, how unbelievable, a European war then seemed,” her friend Alice Hamilton later wrote. “Believing as we did then in the slow but sure progress of the human race, we looked forward to nothing worse than sporadic outbursts in such unknown regions as the Balkans or South America, never in the highly civilized countries of the Europe which we knew so well.”
The onset of a brutal global war in the summer of 1914 shocked Jane Addams and other American pacifists who were certain their cause was gaining widespread acceptance. “Nobody who was not a mature person…can realize now how remote, how unbelievable, a European war then seemed,” her friend Alice Hamilton later wrote. “Believing as we did then in the slow but sure progress of the human race, we looked forward to nothing worse than sporadic outbursts in such unknown regions as the Balkans or South America, never in the highly civilized countries of the Europe which we knew so well.”








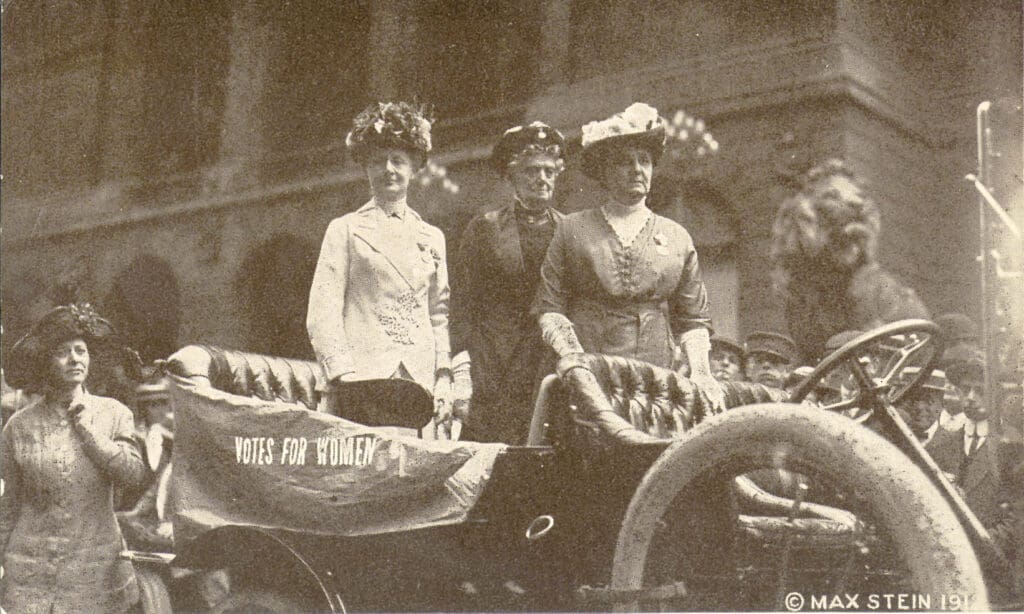
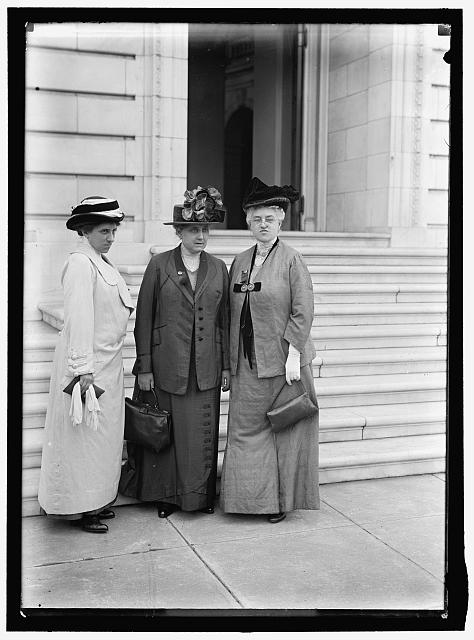
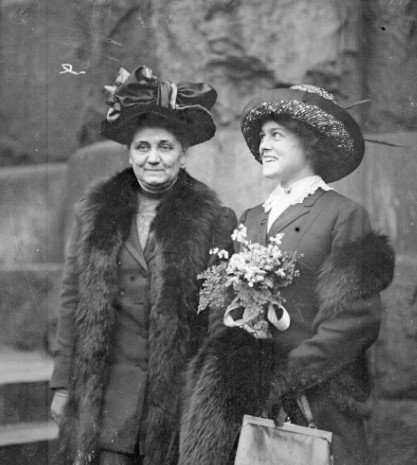
 When we were approached by the Long 19th Amendment team, we were excited to participate for two reasons. Jane Addams isn’t known primarily for her work for woman suffrage. She is often mentioned in lists, or gets a small part in the larger history, but in her day, Addams was a leading suffragist. She was a vice president of the National Woman Suffrage Association and used her considerable fame to promote the movement. She gave frequent speeches on woman suffrage, especially on its
When we were approached by the Long 19th Amendment team, we were excited to participate for two reasons. Jane Addams isn’t known primarily for her work for woman suffrage. She is often mentioned in lists, or gets a small part in the larger history, but in her day, Addams was a leading suffragist. She was a vice president of the National Woman Suffrage Association and used her considerable fame to promote the movement. She gave frequent speeches on woman suffrage, especially on its 